Intermittent fasting, a dietary approach gaining immense popularity, has become a prominent method for enhancing health and managing weight. With an increasing number of people adopting this eating pattern, understanding its benefits is essential. In this discussion, we will explore the various advantages of intermittent fasting in improving overall health and facilitating effective weight management.
Health Improvements through Intermittent Fasting
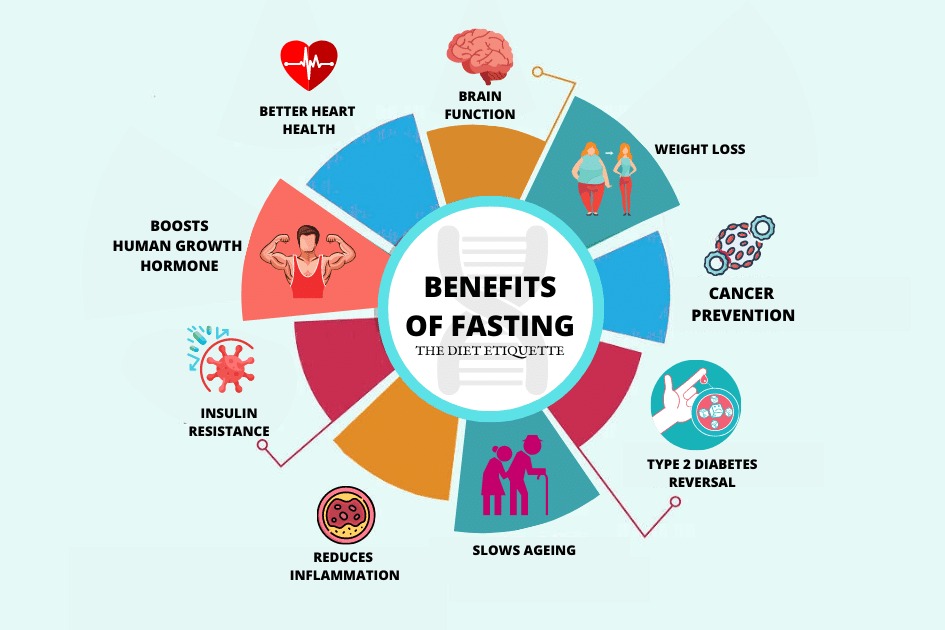
Intermittent fasting has been associated with several notable health improvements that can positively impact overall well-being. One of the key benefits lies in metabolic health, as intermittent fasting has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes. Additionally, the practice triggers autophagy, a cellular cleansing process that promotes cellular repair and longevity.
Furthermore, intermittent fasting has been linked to improvements in cardiovascular health. It helps lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, thus reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Moreover, emerging research suggests potential benefits for brain health, with enhanced brain function and cognitive performance reported among intermittent fasters. There is also speculation regarding its potential to offer protection against neurodegenerative diseases.
Weight Management Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity as a weight management strategy due to its potential to facilitate effective and sustainable weight loss. One of the key mechanisms through which it aids weight management is by increasing fat burning in the body. During fasting periods, the body shifts to using stored fat as its primary fuel source, leading to accelerated weight and fat loss.
Another significant advantage of intermittent fasting is its impact on appetite regulation. By influencing hunger hormones, this eating pattern can help individuals control their caloric intake without feeling deprived. This often results in a reduced overall daily caloric consumption, contributing to weight loss over time.
Unlike some traditional diets that may lead to the loss of muscle mass along with fat, intermittent fasting has been found to preserve lean muscle mass during weight loss. This is crucial for maintaining a healthy metabolic rate and body composition, as muscle tissue plays a vital role in burning calories.
Moreover, intermittent fasting can promote sustainable weight loss by encouraging the development of healthy eating habits. It may help individuals become more mindful of their food choices and eating patterns, leading to a long-term commitment to a healthier lifestyle.
Other Health-Related Benefits
Intermittent fasting has been associated with various other health-related benefits beyond weight management and metabolic improvements. One potential advantage is increased longevity, supported by animal studies showing extended lifespans in organisms following intermittent fasting regimens. While the direct impact on human longevity is yet to be fully understood, the findings are promising and warrant further investigation.
Additionally, intermittent fasting has been linked to improved gut health. During fasting periods, the gut microbiota may experience positive shifts, which can contribute to better digestion and overall gut function. This may be particularly beneficial for individuals with gastrointestinal disorders or imbalances in their gut flora.
There are also psychological and emotional benefits associated with intermittent fasting. Many individuals report reduced stress and anxiety related to food and dieting, as they can develop a healthier relationship with food and gain greater control over their eating habits. Moreover, intermittent fasting has been linked to enhanced mental clarity and focus, potentially attributed to the effects of ketones produced during fasting on brain function.
While these health-related benefits are encouraging, it is essential to recognize that intermittent fasting may not be suitable for everyone, and individual responses can vary. Pregnant women, individuals with eating disorders, or certain medical conditions should exercise caution and seek professional advice before adopting intermittent fasting. Ultimately, considering these potential benefits and risks, intermittent fasting can be a valuable dietary approach for those seeking to improve various aspects of their health and overall well-being.
Considerations and Potential Risks
Before embracing intermittent fasting as a dietary approach, it is essential to consider various factors and potential risks. One crucial consideration is recognizing that intermittent fasting may not be suitable for everyone. Individual variations in metabolism, medical history, and lifestyle play a significant role in determining the effectiveness and safety of this eating pattern.
Different types of intermittent fasting exist, such as the 16/8 method, the 5:2 method, and the eat-stop-eat approach. Each approach has its own set of guidelines and fasting periods, and what works for one person may not work for another. Therefore, understanding one’s personal preferences and needs is vital when selecting an intermittent fasting method.
Ensuring nutritional adequacy during eating windows is another crucial consideration. Individuals must strive to maintain a balanced diet that provides essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals to support their overall health. Fasting should not lead to nutrient deficiencies or other health complications.
Individuals with specific health conditions, such as diabetes, hypoglycemia, or a history of eating disorders, should exercise caution and consult with healthcare professionals before attempting intermittent fasting. It may not be appropriate or safe for certain medical situations.
Potential negative effects should also be acknowledged. Some individuals may experience adverse reactions to intermittent fasting, such as dizziness, fatigue, or mood swings. In such cases, discontinuing the fasting approach or adjusting the fasting schedule may be necessary.
Conclusion
In conclusion, intermittent fasting is a dietary approach that holds immense promise for improving health and supporting effective weight management. Through various mechanisms, it offers several benefits, including enhanced metabolic health, improved cardiovascular function, and potential protection against neurodegenerative diseases. Moreover, intermittent fasting facilitates weight loss by increasing fat burning, regulating appetite, and preserving lean muscle mass.