Health insurance plays a crucial role in the United States healthcare system, providing financial protection and access to medical services for individuals and families. It helps cover the costs associated with healthcare, including doctor visits, hospital stays, medications, and preventive services. Understanding the types of health insurance available in the USA is important for individuals to make informed decisions about their coverage.
The US healthcare system is a complex combination of public and private entities. While the government provides health insurance programs for specific populations, such as Medicare and Medicaid, many Americans obtain coverage through their employers or purchase individual plans. The Affordable Care Act (ACA), enacted in 2010, also expanded access to health insurance through the establishment of health insurance marketplaces and the introduction of subsidies and consumer protections.
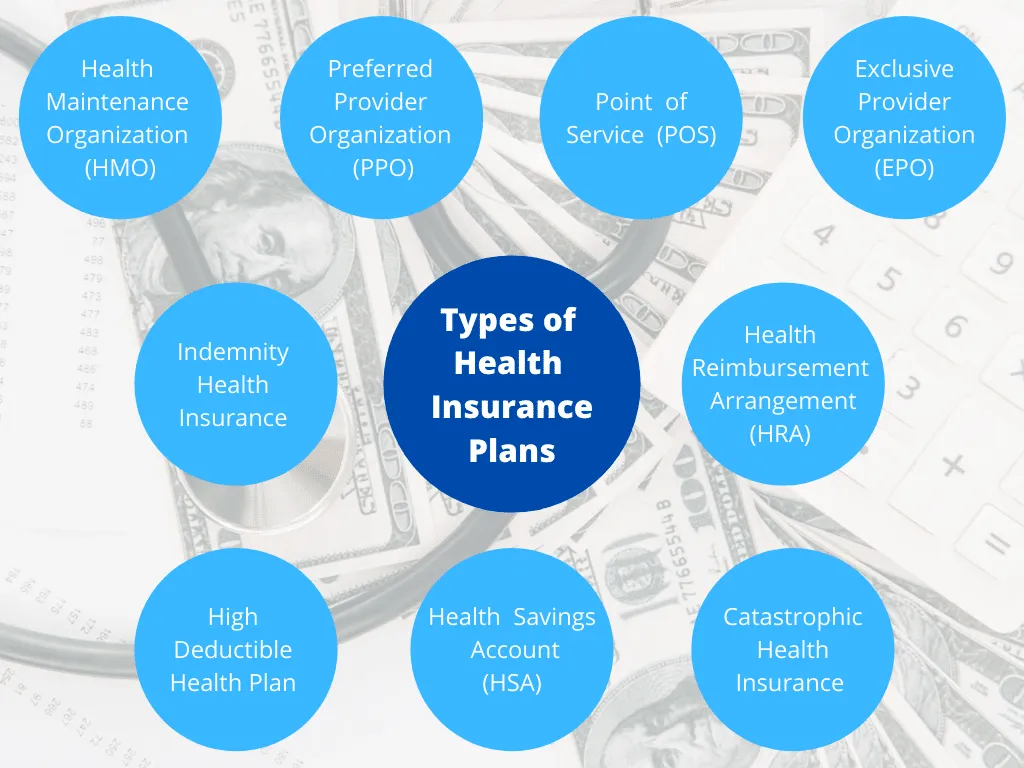
Types of Health Insurance in the USA
A. Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance:
- Definition and characteristics: Health insurance plans offered by employers to their employees as part of their employee benefits package.
- Eligibility and enrollment: Employees who meet certain criteria, such as working full-time or meeting a waiting period, are eligible to enroll in employer-sponsored plans.
- Cost-sharing arrangements: Employers and employees share the cost of premiums, deductibles, and co-payments.
- Benefits and coverage options: Employers offer a range of plan options, including different levels of coverage, networks, and benefits.
B. Individual Health Insurance:
Definition and characteristics: Health insurance plans purchased by individuals and families directly from insurance companies or through the Health Insurance Marketplace.
Marketplace plans (ACA):
- Qualified Health Plans (QHP): Plans that meet the standards set by the ACA, providing essential health benefits and meeting certain consumer protections.
- Premium subsidies and cost-sharing reductions: Financial assistance available to eligible individuals and families to reduce premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
- Essential Health Benefits (EHB): Categories of benefits that must be included in ACA-compliant plans, including preventive care, hospitalization, prescription drugs, and more.
Non-marketplace plans:
- Short-term health plans: Temporary coverage for individuals in transition or with short-term insurance needs but may have limited benefits.
- Catastrophic health plans: Designed for individuals under 30 or with hardship exemptions, providing coverage for essential health benefits after a high deductible is met.
- Enrollment options and eligibility criteria: Enrollment can be done during the annual Open Enrollment Period or Special Enrollment Period triggered by qualifying life events.
C. Government-Sponsored Health Insurance:
Medicare:
- Parts A, B, C, and D: Different components of Medicare, including hospital insurance (Part A), medical insurance (Part B), Medicare Advantage (Part C), and prescription drug coverage (Part D).
- Eligibility and enrollment: Generally available for individuals aged 65 and older, certain younger individuals with disabilities, and those with end-stage renal disease.
Medicaid:
- a. Eligibility criteria: State-administered program providing health coverage for low-income individuals and families, with eligibility criteria varying by state.
- b. Expansion under the Affordable Care Act (ACA): The ACA expanded Medicaid eligibility to include more low-income individuals, with some states choosing to expand and others not.
Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP):
- a. Purpose and eligibility: Provides health coverage to children in low-income families who do not qualify for Medicaid.
- b. Coverage options: CHIP offers comprehensive benefits tailored to children’s healthcare needs.
D. Military and Veterans Health Insurance:
TRICARE:
Eligibility and coverage options: Health insurance program for military service members, retirees, and their dependents, offering multiple plans and coverage options.
Veterans Health Administration (VHA):
- VA health care benefits: Comprehensive healthcare services provided to eligible veterans, including hospital care, outpatient services, mental health care, and more.
- Eligibility and enrollment: Veterans must meet certain criteria based on their service, disability status, income, or other factors to access VHA services.
E. Other Health Insurance Options:
COBRA continuation coverage:
- Eligibility and duration: Allows individuals to continue their employer-sponsored coverage temporarily after leaving a job, but at their own expense.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs):
- Purpose and tax advantages: Tax-advantaged savings accounts paired with high-deductible health plans, allowing individuals to save money for medical expenses.
- Eligibility and contributions: Specific criteria must be met to open and contribute to an HSA, with annual contribution limits.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of health insurance available in the USA is crucial for individuals and families to make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage. Health insurance options range from employer-sponsored plans and individual marketplace plans to government-sponsored programs like Medicare, Medicaid, and CHIP. Additionally, military and veterans have specialized health insurance options such as TRICARE and VHA.
Factors to consider when choosing health insurance include premiums, deductibles, out-of-pocket costs, network coverage, provider choices, prescription drug coverage, specialized services and treatments, plan flexibility, and limitations. It is important to evaluate these factors based on individual needs, budget, and healthcare requirements.


Leave a Comment
Instagram