Health insurance plays a vital role in the United States, providing financial protection against the high costs of medical care. As healthcare expenses continue to rise, it is essential to understand the average cost of health insurance in the USA. This article will explore the factors that influence health insurance costs, examine the average costs based on plan types and age groups, analyze regional variations, discuss the impact of pre-existing conditions, suggest strategies for reducing costs, and touch upon future trends in health insurance expenses.
Factors Affecting Health Insurance Costs
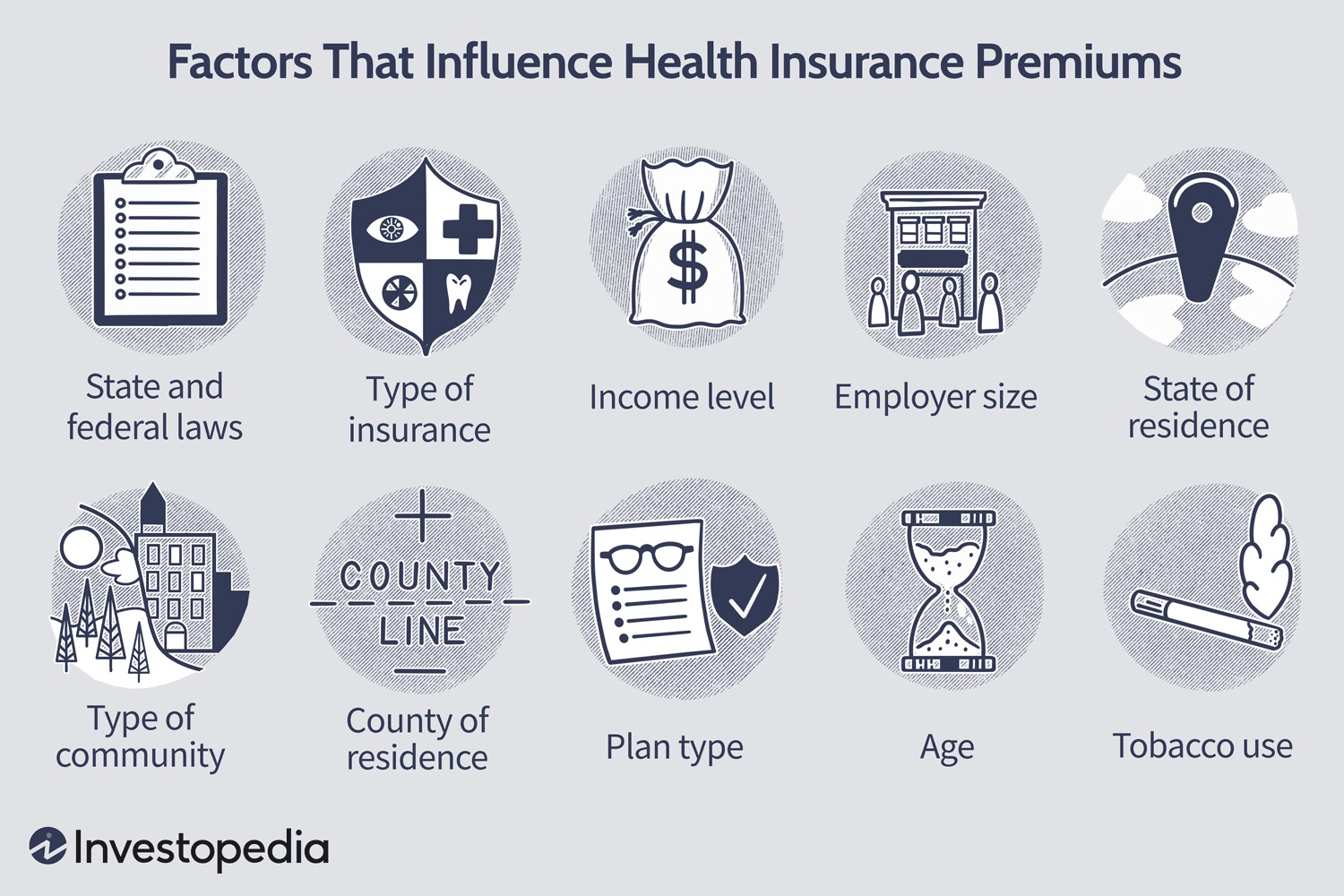
The cost of health insurance in the United States can vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these factors is essential for individuals to evaluate and anticipate their health insurance expenses. Here are some key factors that influence health insurance costs:
A. Age and Demographic Factors:
- Younger individuals typically have lower health insurance premiums compared to older adults due to lower healthcare utilization rates.
- Gender can also impact costs, as some states allow insurers to consider gender when determining premiums.
B. Geographic Location:
- Health insurance costs vary across different regions and states in the USA.
- Areas with higher healthcare costs, such as metropolitan areas, tend to have higher insurance premiums.
C. Type of Health Insurance Plan:
- Health insurance plans can be categorized as HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations), PPOs (Preferred Provider Organizations), or EPOs (Exclusive Provider Organizations), among others.
- Each plan type has different cost structures, including premiums, deductibles, copayments, and out-of-pocket maximums.
D. Employer-Sponsored vs. Individual Plans:
- Employer-sponsored health insurance plans often offer lower premiums as employers typically contribute a portion of the premium.
- Individual plans purchased directly from insurance providers or through the Health Insurance Marketplace can have higher premiums but provide more flexibility.
E. Pre-existing Conditions:
- Prior medical conditions can significantly impact health insurance costs.
- Before the Affordable Care Act (ACA), insurers could deny coverage or charge higher premiums based on pre-existing conditions. However, the ACA prohibits such practices and provides protections for individuals with pre-existing conditions.
Average Cost of Health Insurance by Plan Type
The average cost of health insurance in the United States varies depending on the type of plan individuals or families choose. Different plan types offer varying levels of coverage and cost-sharing arrangements. Let’s explore the average costs associated with two common plan types: employer-sponsored health insurance and individual health insurance.
A. Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance:
Premiums: The average annual premium for employer-sponsored health insurance for single coverage was around $7,470 in 2020, with employers contributing an average of 77% of the premium cost. For family coverage, the average annual premium was approximately $21,342, with employers covering around 70% of the cost.
Deductibles and Copayments: Employer-sponsored plans often involve cost-sharing in the form of deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance. The average annual deductible for employer-sponsored plans was about $1,644 for single coverage and $4,428 for family coverage in 2020.
Employer Contributions: Employers typically contribute a significant portion of the premium cost for their employees, reducing the burden on individuals. The average employer contribution towards the premium was around 83% for single coverage and 73% for family coverage in 2020.
B. Individual Health Insurance:
Premiums: The average monthly premium for individual health insurance plans purchased through the Health Insurance Marketplace (Exchange plans) was $452 in 2021. However, premium costs can vary significantly based on factors such as age, location, and plan level (Bronze, Silver, Gold, or Platinum).
Deductibles and Copayments: Individual health insurance plans also involve cost-sharing, including deductibles and copayments. Deductibles can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars per year, depending on the plan.
Subsidies and Tax Credits: Individuals with lower incomes may qualify for subsidies and tax credits to help reduce their health insurance costs. These financial assistance programs are based on income and can significantly lower premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the average cost of health insurance in the USA is essential for individuals, families, and policymakers. Several factors influence health insurance costs, including age, geographic location, plan type, employer sponsorship, and pre-existing conditions. These factors contribute to the wide variation in health insurance expenses across different individuals and regions.
Employer-sponsored health insurance typically offers lower premiums, with employers contributing a significant portion of the cost. On the other hand, individual health insurance plans purchased through the Health Insurance Marketplace can have higher premiums but offer more flexibility.